Accidents can expose the body to sudden mechanical forces that disrupt joints, muscles, ligaments, and nerves. However, these effects are not always immediately noticeable. In many cases, symptoms appear gradually as inflammation increases and tissues respond to trauma. Therefore, seeking a structured clinical evaluation is essential for identifying injuries early and guiding appropriate treatment. Professional personal injury chiropractic Orlando care focuses on biomechanical analysis, neuromuscular function, and evidence-based rehabilitation methods to support recovery.
Clinicians at Winter Park Chiropractic apply a diagnostic and functional approach to injury management. Rather than emphasizing quick symptom suppression, their methodology centers on understanding injury mechanisms, restoring structural balance, and monitoring physiological responses to therapy. Patients from Orlando and neighboring areas such as Winter Park are assessed through systematic examination protocols designed to evaluate joint motion, tissue integrity, and neurological function.
Trauma Mechanics in Musculoskeletal Injuries
When the body experiences sudden acceleration, deceleration, or rotational force, energy transfers through connective tissues and skeletal structures. Consequently, tissues may stretch beyond their normal physiological limits. This can lead to:
- Microtears in muscle fibers
- Ligament strain or sprain
- Joint capsule irritation
- Disc compression or displacement
- Nerve root irritation
From a biomechanical perspective, even low-velocity incidents can generate sufficient force to disrupt alignment or create tissue stress. Therefore, injury assessment must consider both the magnitude of impact and the direction of force transmission through the body.
Why Symptoms May Appear Hours or Days Later
Immediately after trauma, the nervous system releases stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol. These chemicals temporarily reduce pain perception and increase alertness. As a result, injured individuals may feel relatively normal at first. However, once hormone levels stabilize, inflammatory responses begin. Swelling, stiffness, and discomfort often develop later because:
- Damaged tissues release inflammatory mediators
- Muscles tighten to protect injured areas
- Joint movement becomes restricted
- Nerve sensitivity increases
For this reason, delayed symptoms are common after accidents, making early clinical assessment particularly important even when pain is mild or absent.
Common Trauma-Related Conditions Evaluated Clinically
Injury-focused chiropractic assessment frequently identifies several categories of trauma-related dysfunction.
Cervical Acceleration–Deceleration Injury
Commonly associated with sudden head movement, this condition affects cervical ligaments, facet joints, and stabilizing muscles. Biomechanically, rapid motion places stress on soft tissues that control neck stability.
Lumbar Compression or Strain
Lower back structures absorb significant force during impact. Consequently, discs, paraspinal muscles, and ligaments may become inflamed or strained.
Myofascial Injury
Microscopic tears in muscle and fascia can alter movement patterns. Over time, these changes may lead to compensatory strain in surrounding tissues.
Intervertebral Disc Stress
When compressive forces exceed disc tolerance, the disc may bulge or herniate, potentially affecting nearby nerve roots.
Joint Motion Restriction
Impact can reduce joint mobility by causing inflammation or structural imbalance. Restricted movement often contributes to stiffness and discomfort.
Clinical Assessment Methods Used in Injury Evaluation
Accurate diagnosis requires structured examination rather than assumption. Clinical chiropractic evaluations typically include:
- Static posture assessment
- Dynamic movement analysis
- Palpation of soft tissues and joints
- Neurological reflex testing
- Orthopedic stress tests
When indicated, imaging studies may be recommended to visualize structural changes. Because each test measures a different physiological parameter, combining them improves diagnostic accuracy.
Evidence-Based Therapeutic Interventions
Treatment protocols for trauma-related injuries often integrate multiple modalities selected according to clinical findings. Common therapeutic approaches include:
- Manual spinal adjustments — These controlled forces aim to restore joint mobility and normalize mechanical function.
- Soft tissue mobilization — Mechanical pressure may reduce muscle tension and improve circulation.
- Rehabilitative exercise therapy — Targeted movement programs can strengthen stabilizing muscles and improve coordination.
- Neuromuscular retraining — Structured exercises help restore normal communication between nerves and muscles.
- Postural re-education — Corrective strategies address biomechanical stress patterns during daily activities.
Because each modality affects different physiological systems, combining them often produces more comprehensive outcomes.
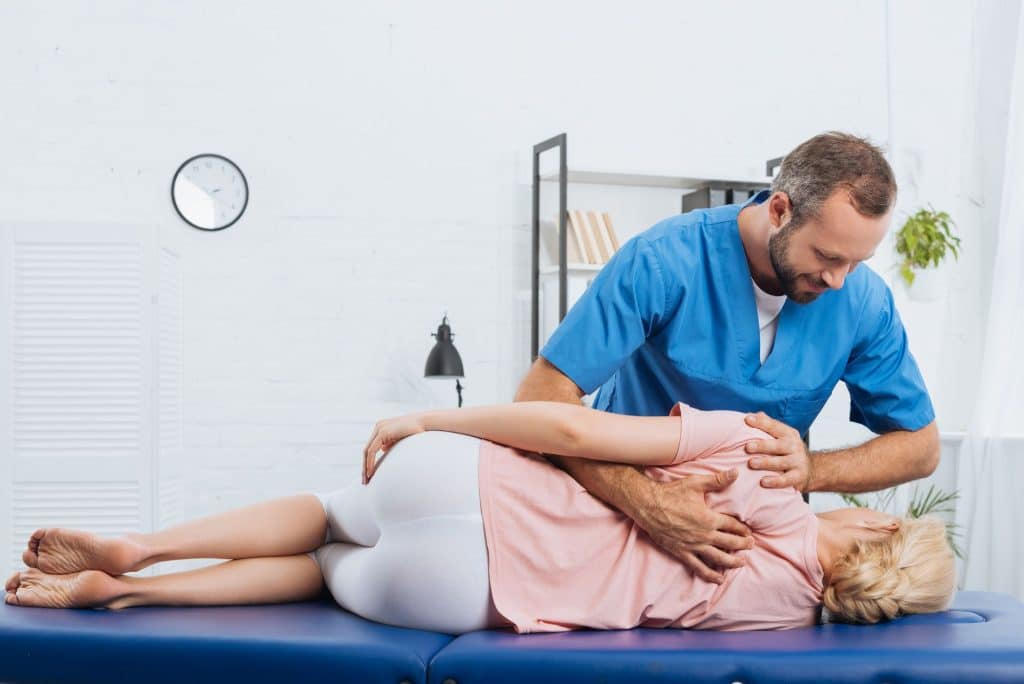
Physiological Effects of Chiropractic Interventions
Research suggests that when manual therapies are properly applied, they can influence the body through multiple physiological mechanisms. These include increasing joint range of motion, enhancing blood flow to affected tissues, reducing excessive muscle tension, modulating pain signaling pathways, and supporting proprioceptive function. Although individual responses may vary, collectively these physiological effects can contribute to improved mobility, better functional performance, and a noticeable reduction in discomfort when treatment is administered correctly.
Clinical Documentation in Injury Management
From a medical perspective, maintaining detailed records is essential for monitoring patient progress and guiding effective care. Structured documentation typically includes baseline functional measurements, pain scale assessments, range-of-motion data, neurological findings, and observed responses to treatment over time. This information enables practitioners to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions and make necessary adjustments to treatment plans. Moreover, objective records serve an important role in supporting insurance claims or legal proceedings following accidents.
Technology Supporting Diagnostic Precision
Modern musculoskeletal clinics often incorporate technology to enhance evaluation accuracy. Tools sometimes used in clinical settings include:
- Digital posture analysis systems
- Surface electromyography for muscle activity measurement
- Motion analysis software
- Therapeutic ultrasound devices
- Electrical stimulation equipment
These technologies provide quantifiable data that can guide treatment decisions and track measurable improvement.
Indicators That Warrant Professional Evaluation
Certain post-trauma symptoms suggest underlying musculoskeletal dysfunction and should be assessed clinically:
- Persistent or worsening headaches
- Neck or back stiffness
- Radiating pain into limbs
- Tingling or numbness
- Limited range of motion
- Pain interfering with sleep
These signs may indicate structural or neurological involvement requiring professional examination.
Stages of Functional Recovery After Injury
Rehabilitation typically progresses through predictable physiological phases. Understanding these stages helps explain why recovery requires time and structured care.
Inflammatory Phase
Immediately after injury, tissues swell and become sensitive as the immune system initiates repair.
Repair Phase
Fibroblasts generate new connective tissue fibers to replace damaged structures.
Remodeling Phase
New tissue reorganizes and strengthens in response to controlled movement and mechanical load.
Functional Restoration Phase
Muscles, joints, and nerves regain coordination and stability, allowing normal activity.
Each phase requires different therapeutic strategies; therefore, treatment plans often evolve as healing progresses.
Distinguishing Injury Specialists from General Musculoskeletal Providers
Practitioners who focus on trauma cases typically develop deeper familiarity with injury biomechanics and post-accident pathology. Their assessments often emphasize:
- Force vectors involved in impact
- Tissue tolerance thresholds
- Delayed-onset injury patterns
- Functional impairment measurement
This analytical approach allows for more precise clinical reasoning when designing rehabilitation programs.
Patient Participation in Recovery Outcomes
Scientific evidence consistently demonstrates that patient engagement plays a critical role in the success of rehabilitation. Active participation may involve performing prescribed exercises, maintaining proper posture, following activity guidelines, and attending scheduled evaluations. Since tissue adaptation relies on controlled mechanical stimulation, consistent adherence to these therapeutic recommendations significantly supports optimal healing and long-term functional recovery.
Preventive Biomechanics After Recovery
Once healing is complete, maintaining musculoskeletal health becomes a priority. Preventive strategies often focus on reducing mechanical stress through:
- Ergonomic adjustments
- Strength and flexibility training
- Movement pattern correction
- Postural awareness
These measures help distribute forces evenly across joints and tissues, lowering the likelihood of reinjury.
Clinical Perspective on Personalized Treatment Planning
No two injuries are identical. Consequently, individualized care plans are based on measurable findings rather than generalized assumptions. Variables considered during planning include:
- Injury mechanism
- Tissue involvement
- Functional limitations
- Baseline physical condition
- Response to initial treatment
Tailoring therapy to these factors improves both safety and effectiveness.
Restoring Function Through Structured Musculoskeletal Care
Trauma-related injuries involve complex physiological processes that require systematic evaluation and evidence-informed management. Professional personal injury chiropractic Orlando services provide a framework for analyzing injury mechanics, monitoring tissue healing, and guiding rehabilitation progression.
Through structured assessment, targeted therapy, and measurable outcome tracking, clinical chiropractic care aims to restore joint mobility, muscular balance, and neurological coordination. Ultimately, the goal is not merely symptom reduction but functional recovery that supports long-term musculoskeletal health.



